Creation Date
1836
Height
11 cm
Width
19 cm
Medium
Genre
Description
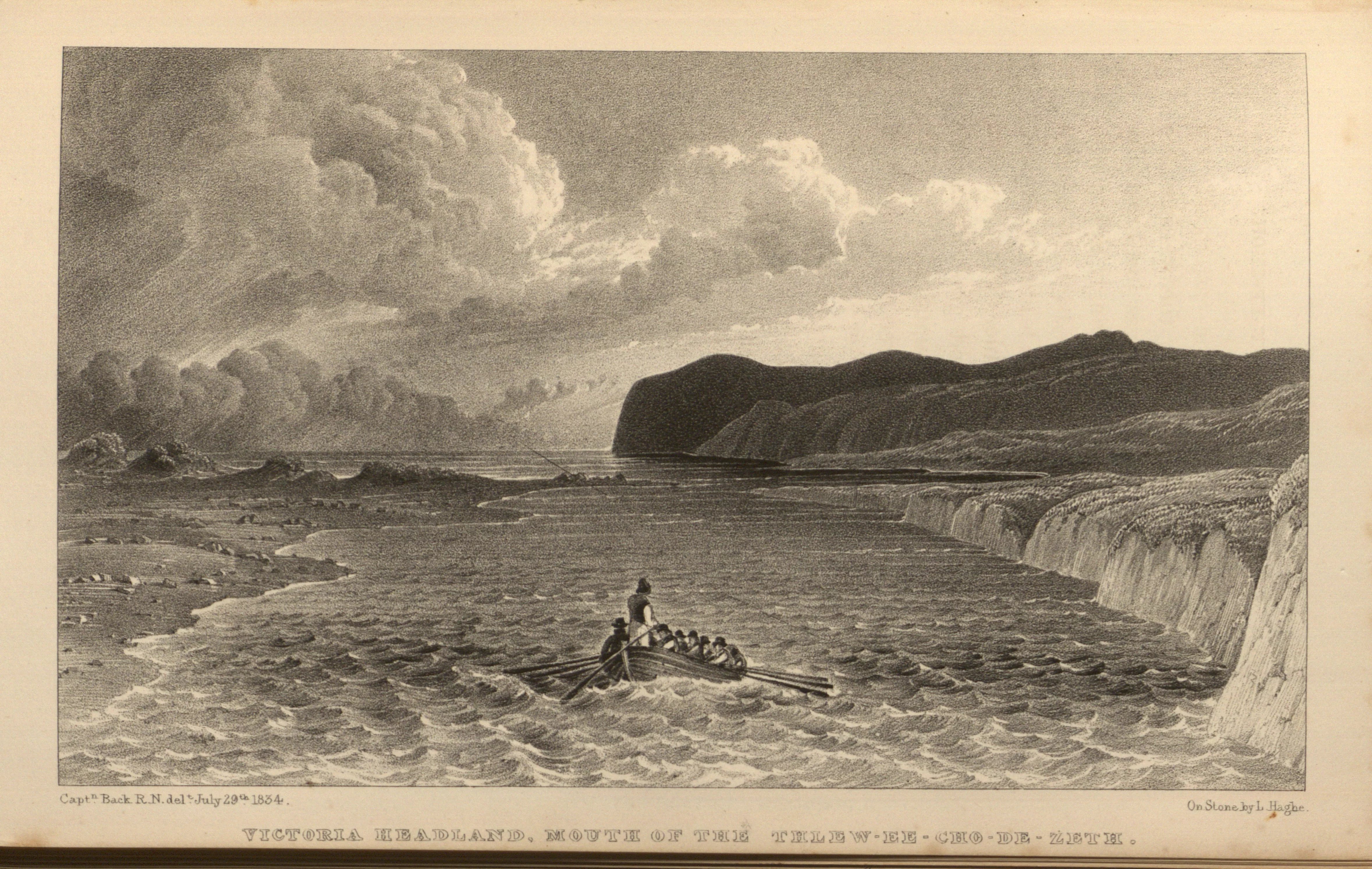
Sir George Back's Victoria Headland effectively places the British Empire in a relation of unique, solitary independence to the Arctic landscape which, rather than acting as an impediment to imperial movements, placidly funnels the explorers' rowboat along the river towards the sea.
A crew rows their boat away from the viewer and towards the mouth of a river in lightly choppy seas. A man standing in back steers with the rudder oar. A sand beach extends on the left, while bluffs rise to the right. Billowing clouds build on the horizon to the left. It appears to be sunset or sunrise, the sun itself hidden behind the bluffs.
The Royal Geographic Society (RGS) was established in 1830. It "increasingly took responsibility for both promoting polar research and publishing the results"; furthermore, "one of the first expeditions the Society supported was that of Sir George Back to the Canadian Arctic in 1832” (David 63-6). The RGS also produced the Proceedings Journal and then the Geographical Journal in order to record expeditions, provide illustrations, and provide information for new explorers, as well as to provide interim reports on those expeditions (David 63-6).
Stuart C. Houston notes that:
The world’s greatest naval power and its underemployed navy after the end of the Napoleonic Wars found the continued presence of large blank areas on the world map an irresistible challenge. John Barrow, the powerful second secretary to the Admiralty, had strong backing from the newly important scientific community to renew the search for the Northwest Passage after a long wartime hiatus. (xiv)
In addition to simply providing visual aids for a travel narrative, then, Back’s images must be seen as integral to the literal illustration of those “large blank areas” that Britain wanted to conquer. Expedition imagery during the Romantic period addressed other needs as well, including the translation of “otherness”—which the Arctic so easily exemplified in its comparatively uninhabited starkness—into a culturally understandable, and thus accessible, space for national expansionism and the application of identity. Furthermore, in ostensibly drawing accurate portrayals of the landscape (which Franklin frequently confirms), Back created scientific records designed to both titillate and inform the British public and scientific community.
This is one of Back's most strikingly imperialist images, which—even before it was printed in his book—was made more so by his naming the landscape after a monarch. The rowboat with the explorers is, moreover, effectively alone and unimpeded by the Arctic landscape. Back writes:
The afternoon permitted us to proceed; and it was while threading our way between some sand-banks, with a strong current, that we first caught sight of a majestic headland in the extreme distance to the north, which had a coast-like appearance. This important promontory was subsequently honored by receiving the name of Her Royal Highness the Princess Victoria. The sand-banks also now became broken into cliffs, which, dwindling away on the eastern side to a vanishing point, subsided on the western into low flats, the level of which was just broken by half a dozen sandy knolls sparingly tipped with a few blades of dry grass . . . This then may be considered as the mouth of the Thlew-ee-choh, which, after a violent and tortuous course of five hundred and thirty geographical miles, running through iron-ribbed country without a single tree on the whole line of its banks, expanding into fine large lakes with clear horizons, most embarrassing to the navigator, and broken into falls, cascades and rapids, to the number of no less than eighty-three in the whole. (389-390)
Back's description indicates his frequently inconsistent style, which variously displays aesthetic word-paintings, imperialist haughtiness, and simple yet detailed cartographic diction. This image is also a prime example of the capabilities of the lithographer Louis Haghe, who is clearly showing off his artistic ability and the flexibility of the medium in the beautiful, complex forming of the clouds.
Locations Description
The Thlew-ee-cho-de-zeth, or Great Fish River, is now called the "Back River" after George Back:
Back River rises in drift-covered hills northeast of Great Slave Lake and flows north and east through a low featureless plain that has numerous sandy areas and long eskers. Northward the lowland merges into the rocky hills of the Bathurst Upland and the drumlinoid hills south of Queen Maud Gulf. (An Introduction to the Geography of The Canadian Arctic 5)
Publisher
Day & Haghe
Collection
Accession Number
Thordarson T 183
Additional Information
Bibliography
Ames, Van Meter. “John Dewey as Aesthetician.” The Journal of Aesthetics and Art Criticism 12.2 (1953): 145-68. Print.
Back, George. Arctic Artist: The Journal and Paintings of George Back, Midshipman with Franklin, 1819-1822. Ed. C. Stuart Houston. Buffalo: McGill-Queen’s UP, 1994. Print.
---. Narrative of the Arctic Land Expedition to the Mouth of the Great Fish River and along the Shores of the Arctic Ocean, in the Years 1833, 1834, and 1835. London: 1836. Print.
Broglio, Ron. Technologies of the Picturesque: British Art, Poetry, and Instruments, 1750-1830. Lewisburg: Bucknell UP, 2008. Print.
Canada Department of Mines and Technical Surveys, Geographical Branch. An Introduction to the Geography of The Canadian Arctic. Edmond Cloutier: Ottawa, 1951. Print.
Daston, Lorraine and Peter Gallison. Objectivity. New York: Zone Books, 2007. Print.
David, Robert G. The Arctic in the British Imagination. New York: Manchester UP, 2000. Print.
Dewey, John. “Experience, Nature and Art.” John Dewey: The Later Works, 1925-53. Ed. Jo Ann Boydston. Carbondale: Southern Illinois UP, 1981. 266-95. Print.
Dewey, John. “The Practical Character of Reality.” Pragmatism: The Classic Writings. Ed. H.S. Thayer. Indianapolis: Hackett, 1982. 275-289. Print.
Feldman, Jessica R. Victorian Modernism: Pragmatism and the Varieties of Aesthetic Experience. New York: Cambridge UP, 2002. Print.
Franklin, John. Narrative of a Second Expedition to the Shores of the Polar Sea, in the Years 1825, 1826, and 1827. London, 1828. Print.
Heringman, Noah, ed. Romantic Science: The Literary Forms of Natural History. Albany: State University of New York Press, 2003. Print. Suny Series in the Long Nineteenth Century.
---. Introduction. Heringman 1-22.
---. “The Rock Record and Romantic Narratives of the Earth.” Heringman 53-85.
Houston, C. Stuart. Introduction. Arctic Artist: The Journal and Paintings of George Back, Midshipman with Franklin, 1819-1822. By George Back. Ed. Houston. Buffalo: McGill-Queen’s UP, 1994. xiii-xxvi. Print.
Labbe, Jacqueline M. Romantic Visualities: Landscape, Gender and Romanticism. London: Macmillan, 1998. Print.
Levin, Jonathan. “The Esthetics of Pragmatism.” American Literary History. 6.4 (1994): 658-83. Print.
Maclaren, I.S. “Commentary: The Aesthetics of Back’s Writing and Painting.” Arctic Artist: The Journal and Paintings of George Back, Midshipman with Franklin, 1819-1822. By George Back. Ed. C. Stuart Houston. Buffalo: McGill-Queen’s UP, 1994. 275-310. Print.
Markham, Sir Clements R. The Lands of Silence: A History of Arctic and Antarctic Exploration. Cambridge: Cambridge UP, 1921. Print.
Meisel, Martin. Realizations: Narrative, Pictorial, and Theatrical Arts in Nineteenth-century England. Princeton: Princeton UP, 1983. Print.
Potter, Russell A. Arctic Spectacles: The Frozen North in Visual Culture, 1818-1875. Seattle: University of Washington Press, 2007. Print.
Price, Uvedale. “Essays on the Picturesque, as compared with the Sublime and the Beautiful; and on the Use of studying Pictures, for the Purpose of improving real Landscape (Vol. 1, 1810)." The Picturesque: Literary Sources and Documents. Vol. 2. Ed. Malcolm Andrews. Robertsbridge: Helm Information, 1994. 72-142. Print.
Rescher, Nicholas. Realistic Pragmatism: An Introduction to Pragmatic Philosophy. Albany: State University of New York Press, 2000. Print.
Steele, Peter. The Man who Mapped the Arctic. Vancouver: Raincoast Books, 2003. Print.
Twyman, Michael. “Haghe, Louis (1806–1885).” Oxford Dictionary of National Biography. Ed. H. C. G. Matthew and Brian Harrison. Oxford: OUP, 2004. Web. 6 Apr. 2009.
Verner, Coolie. Explorers’ Maps of the Canadian Arctic 1818-1860. B.V. Gutsell: Toronto, 1972. Print.
Wilson, Eric. The Spiritual History of Ice. New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2003. Print.
Woodring, Carl. Nature into Art: Cultural Transformations in Nineteenth-Century Britain. Cambridge: Harvard UP, 1989. Print.